

Diffusion is a transport of atoms or molecules caused by their random thermalĬapacity for the lung (D L ) is defined as the volume of gas diffusing through the lung barrier per min and.Leaving the left (or the right) ventricle each min. Uptake of oxygen molecules into the passing pulmonary blood - into the cardiac Regional ventilation-perfusion ratio in health and disease, and peripheral gas To explain the alveolar dead space, veno-arterial shunts, uneven Oxygen uptake and carbon dioxide output, pulmonary vascular resistance and
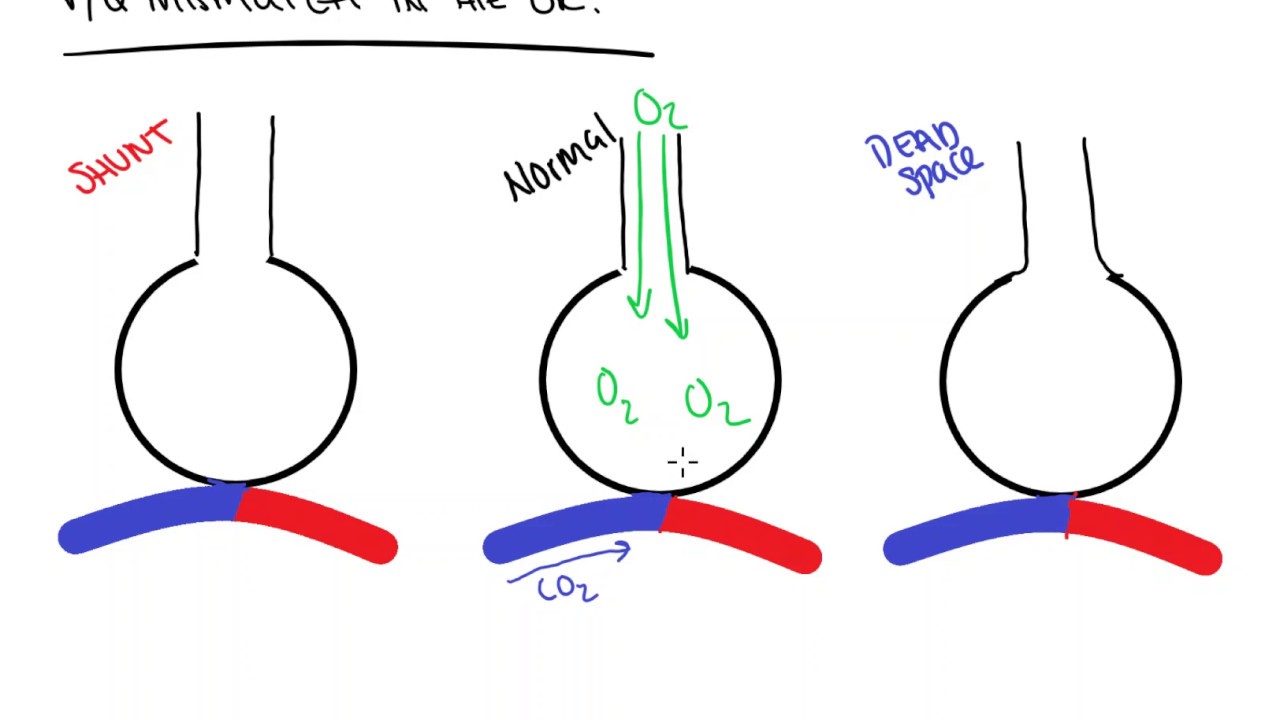
Perfusion, use the alveolar gas equation, the alveolar ventilation equation, theįinal V ° A / Q ° - equation, and the law of mass balance in calculations. Pulmonary perfusion, and its measurements, describe the P O2- P CO2-diagram, hypo-and hyperventilation, pulmonary waterīalance, and mixed venous blood composition. ĭalton’s laws, factors of importance for the lung diffusion capacity and , and the ventilation-perfusion ratio ( V ° A / Q ° -ratio). Hypocapnia, hypoxia, respiratory quotient (RQ), ventilatory exchange ratio( R) Pathophysiology Equations Self-Assessment Answersĭiffusion, diffusion- and perfusion-limited gas exchange, hypercapnia, Study_ Objectives Principles Definitions Essentials New Human Physiology | Paulev-Zubieta 2nd Edition Chapter 14: Gas Exchange and Disorders


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
